A unique consortium of Ethiopian and Dutch expert organizations has recently started a Euro 4.3 million initiative called “Ziway-Shalla: Basin in Balance” in Ethiopia’s Central Rift Valley. This four-year project aims to ensure a balanced Ziway Shalla Basin by improving its water and food security, increasing income for small farmers, and nature conservation. Through multi-dimensional interventions, the project aims to set an example of effective landscape approach to ensure a climate resilient and sustainable Ziway-Shalla basin for people and nature.
Every wetland is part of a bigger water system and its problems should not be viewed separately. In this case, Ziway-Shalla is a closed water sub-basin, comprising the catchments of Ziway, Langano, Abijatta and Shalla lakes. Lake Ziway is the only freshwater lake that feeds lake Abijatta, which forms part of the Abijatta-Shalla National Park and the most important wetland area for migratory water birds in Ethiopia.
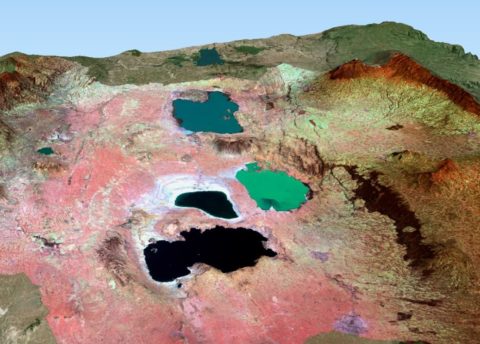
From up to down: Ziway, Langano, Abijatta and Shalla lakes. The white lines in Abijatta lake shows clearly the shrinking water level. Image produced from ESA remote sensing data and processed by Wetlands International.
Overconsumption of water currently poses a threat to the natural water system of the basin. In last two decades, many small farmers and large agribusiness including Dutch and French investments have been increasingly drawing huge amount of water for irrigation from Ziway. As a result, water quality is deteriorating and quantity is declining. Furthermore, erosion caused by unsustainable land use, deforestation and overgrazing in the watershed have aggravated the problems as sediment gradually fills up the lake. If this continues, Lake Abijatta, which has already lost 35% of its surface area since 2000, may disappear within the coming two decades and cause a sharp decline in bird population and water-related economic activities in the area. Households, farmers,

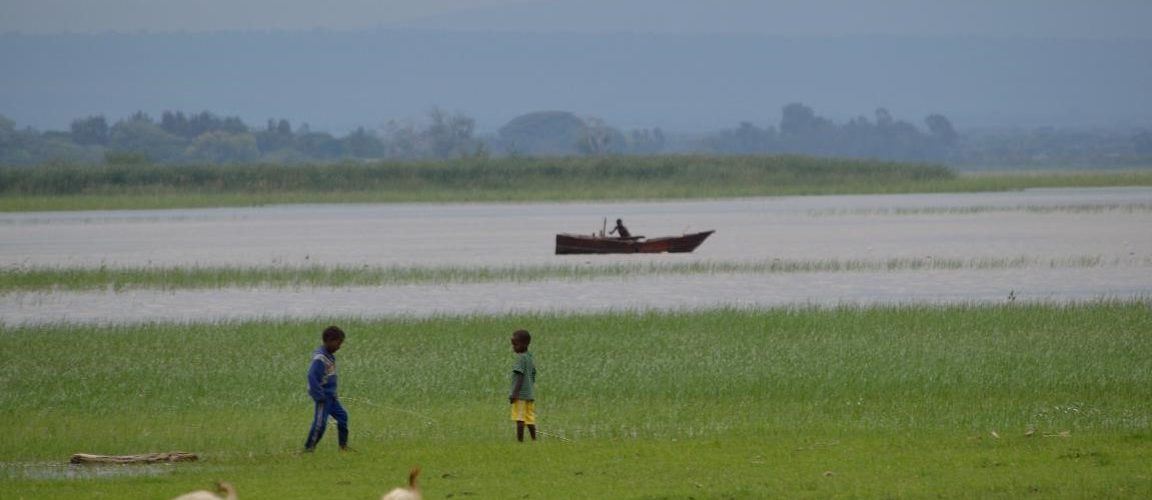
Ziway, the only freshwater lake has become the center for agriculture-based economic activities.
To address this issue, the project aims to use the landscape approach and intervene across the whole sub-basin from four angles: One, efficient irrigation systems through better business cases for farmers; two, a transparent water allocation system; three, prevention of erosion; and four., to build relevant capacity and awareness among stakeholders. Every member of the consortium has a unique role to play. Rift Valley Lake Basin Authority (RVLBA), a local public authority, will work on developing a Water Allocation Plan based on water permits and tariffs.Meki-Batu Cooperatives Union will work toward improved agricultural practice including better irrigation systems that will help raise the productivity and income of its member farmers. Joy-Tech will provide improved planting material and technical expertise to modernize the agriculture practice of the small-scale farmers.
“Ziway Shalla: Basin in Balance” project is a partnership among Wetlands International, Rift Valley Lake Basin Authority, World Waternet Foundation, Acacia Water, MekiBatu Cooperatives and Union and Joytech Plc. Wetlands International, with its experience of Climate Resilient Flyways project in Ethiopia and its knowledge in Landscape approach, will lead the project. This project is funded by the Sustainable Water Fund of the Dutch Enterprise Agency (RVO).

